What is an AI Agent? Benefits, Drawbacks, and More
Updated: by Heysho

AI Agents have emerged as a revolutionary force in the rapidly evolving landscape of generative AI, capturing attention across business sectors and everyday applications alike.
What sets AI Agents apart from traditional AI systems and chatbots is their remarkable capacity to independently make decisions, complete tasks, and enhance their performance by understanding specific objectives.
This guide offers a clear, thorough exploration of AI Agents—covering everything from their core definition to their inner workings, varieties, and cutting-edge applications.
We'll also examine the practical considerations for implementation, including key benefits, potential challenges, and insights into future developments and market trends.
By the end of this article, you'll have gained valuable insights into AI Agents and practical ideas for implementing them in your business operations or personal projects.
Table of Contents
- 1. What is an AI Agent? Basic Concepts Explained
- 2. How AI Agents Work: Understanding the Mechanism
- 3. AI Agents vs. Chatbots: What's the Difference?
- 4. Types of AI Agents: What Kinds Are There?
- 5. Features of AI Agents: What Can They Do?
- 6. Use Cases of AI Agents: How Are They Actually Used?
- 7. Pros and Cons of Implementing AI Agents
- 8. How to Implement AI Agents: A Beginner's Guide
- 9. Featured AI Agent Products and Services
- 10. The Future of AI Agents: What Will Happen Next?
- Summary
1. What is an AI Agent? Basic Concepts and Definitions
The Basic Role and Function of AI Agents
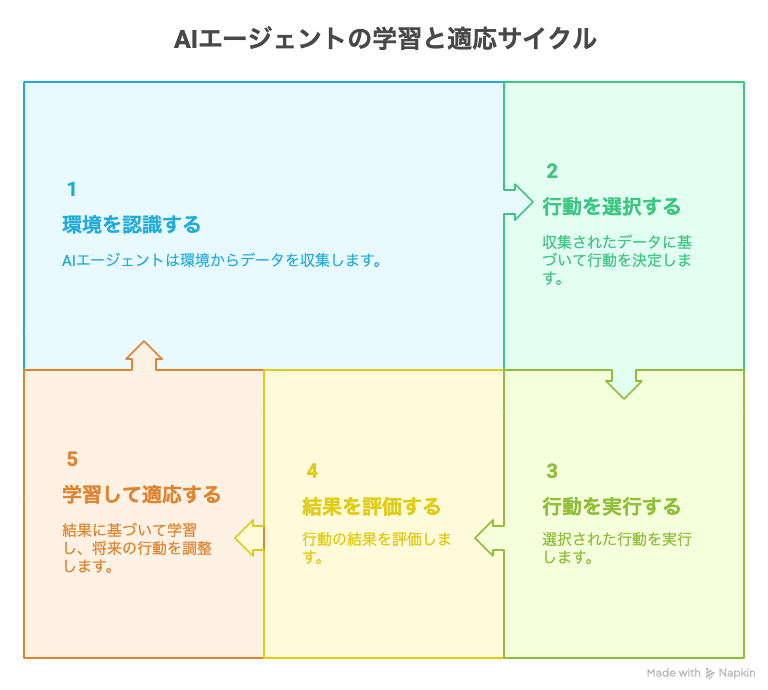
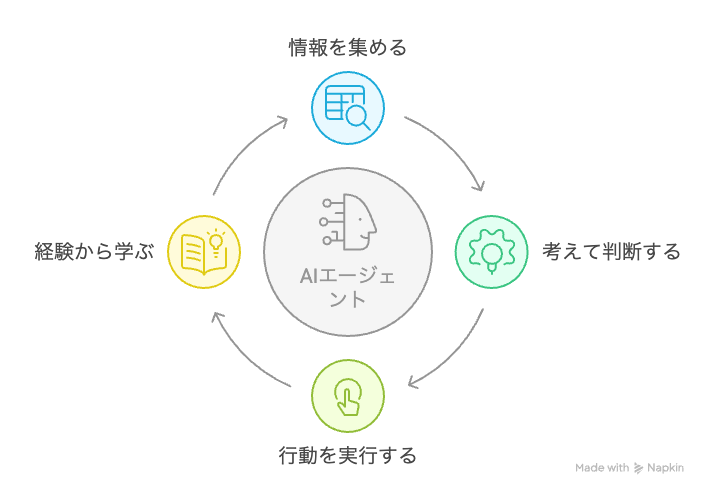
An AI agent is an AI system that perceives its surrounding environment, autonomously selects and executes actions to achieve objectives, and continues to learn and adapt in the process. In simple terms, it can be easily understood as "AI that can think and act on its own."
The word "agent" originally means "proxy" or "actor." For example, just as a real estate agent searches for properties on behalf of a client, an AI agent is responsible for making judgments and executing tasks on behalf of humans. Furthermore, a major feature of AI agents is their ability to learn from experience and continuously improve themselves.
What is the Difference Between Traditional AI and AI Agents?
Single-Task Oriented vs. Goal-Achieving
Traditional AI has been specialized in single tasks such as "determining whether this photo is a dog or a cat" or "writing a sentence on a given theme."
On the other hand, AI agents aim to achieve complex goals such as "planning a weekend trip" by combining multiple means such as information gathering, comparison of options, and reservation procedures to achieve the final goal.
Ability to Judge and Act Independently
While traditional AI follows detailed rules such as "if ○○, then ××," AI agents think for themselves about "what is needed to make a comfortable trip" and explore and execute the optimal action based on information obtained from the environment.
For example, it is possible to respond flexibly, such as checking the weather forecast and suggesting indoor activities in case of rain.
Ability to Respond to Changes in Circumstances
AI agents constantly incorporate new information from web APIs, sensors, user feedback, etc., and respond to changes in circumstances.
For example, an AI agent that performs stock price analysis can monitor market data in real time and automatically adjust its investment strategy if there are sudden market fluctuations.
2. How AI Agents Work: The Building Blocks of Brain and Body
Basic Structure and Functionality of AI Agents
AI agents are composed of four basic elements that mirror the human thought process:
Function to Gather Information (Perception)
Similar to human senses, this function acquires external information through text input, voice recognition, camera images, and various sensors.
For example, a smart home agent might detect "the current temperature is 25°C" from a room sensor.
Function to Think and Judge (Thinking and Planning)
This component analyzes collected information alongside past knowledge to formulate optimal action plans for achieving goals.
For instance, it might determine "the set temperature is 22°C, so the air conditioner needs to be activated to lower the temperature."
Function to Act (Execution)
This is where the agent implements its decisions by issuing system commands, controlling physical components, or generating outputs.
Following our example, the execution would be "turning on the air conditioner and setting it to cooling mode."
Function to Learn from Experience (Learning)
The agent evaluates results, learns from successes and failures, and applies these insights to future decisions.
It might remember that "the target temperature was reached in 30 minutes after activating the air conditioner," enabling more efficient responses in similar situations.
Four Core Technologies Powering AI Agents
Foundation of Pattern Recognition: Machine Learning/Deep Learning
This technology enables prediction, classification, and content generation by identifying patterns in large datasets.
For example, it can learn from purchase history that "this customer has a strong interest in health foods" and recommend relevant products.
Language Understanding: Natural Language Processing (NLP)
This technology allows agents to comprehend human language and respond appropriately.
It can understand a question like "What's tomorrow's weather in Tokyo?" and retrieve forecast data to provide an answer.
Experience-Based Learning: Reinforcement Learning
This method helps agents learn optimal behaviors through trial and error, maximizing positive outcomes.
Like chess AI that improves with each game, it develops adaptability to changing environments.
External Service Integration: API Connectivity
This technology significantly expands agent capabilities by connecting with external services.
By integrating with calendar, email, and payment APIs, an agent can seamlessly handle complex tasks like "booking a meeting room, notifying participants, and arranging catering."
3. Differences Between AI Agents and Chatbots: What is Fundamentally Different?
Limitations of Traditional Chatbots: Can Only Provide Predetermined Responses
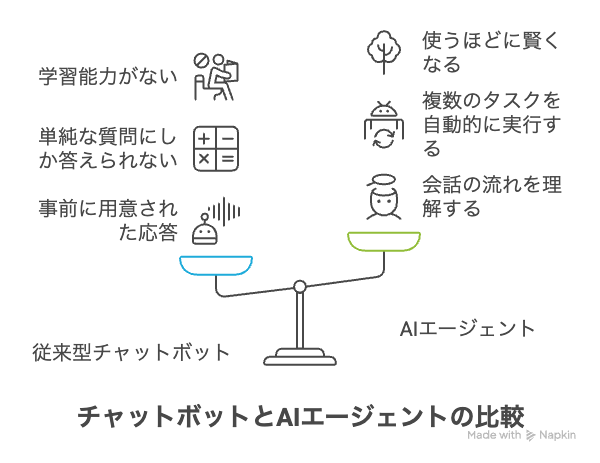
Bound by Pre-Prepared Response Patterns
Traditional chatbots operate within a framework of pre-set dialogue patterns and FAQs, making them unable to handle unexpected questions or complex requests effectively.
For instance, while they can answer "What is the weather tomorrow?", they struggle with nuanced queries like "If it rains tomorrow, how should I adjust my weekend travel plans?"
Designed for Simple Question Answering
Chatbots excel at basic inquiries such as "What are your business hours?" or "How do I return a product?" However, they fall short when faced with multi-step tasks or requests requiring judgment, like "Analyze my recent purchases and recommend products that match my preferences."
Advantages of AI Agents: Intelligent Assistants that Think and Act
Contextual Understanding and Memory
AI agents comprehend entire conversations by connecting current interactions with past dialogue and external information sources.
For example, when asked "Can I book the Nasu Ryokan we discussed last week?", an AI agent can identify the specific ryokan from previous conversations and check its availability.
Seamless Multi-Task Coordination
From a single instruction, AI agents can orchestrate and execute multiple related tasks automatically.
When instructed to "Set up next week's meeting," an agent can check participants' schedules, reserve a room, prepare an agenda, and send invitation emails—all without further input.
Adaptive Learning and Personalization
AI agents continuously learn from interactions, becoming more personalized and efficient over time.
For example, after noticing a pattern of weekly report requests, an agent might proactively ask, "Would you like me to prepare your usual Monday report?"
Real-World Comparison: Shopping Support
Consider these contrasting approaches to online shopping assistance:
• Chatbot: "To return an item, please follow these steps..." (Static, predetermined response)
• AI Agent: "I notice the sneakers you bought last week might not be the right size. We have one size larger in stock if you'd like to exchange them, or I can help process a refund instead. What would you prefer?" (Analyzes purchase history, anticipates needs, offers personalized solutions)
4. Types of AI Agents: Classification by Purpose and Form
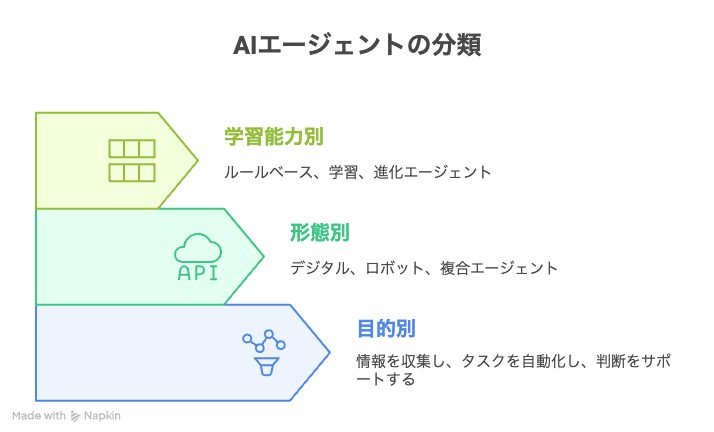
AI Agents by Goal: What They Are Made For
Agents that Collect and Organize Information
These agents collect and organize necessary data from multiple information sources such as the internet and internal databases.
For example, in response to the instruction "Summarize the latest market research report," it can comprehensively search web articles, internal past data, and industry reports, extract key points, and summarize them.
Agents that Automatically Execute Tasks
These agents automate routine tasks and workflows.
For example, it automatically performs repetitive tasks such as "aggregate sales data every Monday and send it to the team" without human intervention.
It helps to streamline time-consuming and monotonous tasks such as invoice processing, data entry, and schedule coordination.
Agents that Support Decision-Making
These agents analyze data and provide decision-making materials using predictive models.
For example, an investment advisor agent can analyze market data and individual asset conditions and make specific proposals such as "The current portfolio is too risky, so we recommend increasing the proportion of bonds by 10%."
It assists in evaluating options in complex situations.
Agents that Respond Through Conversation
These agents interact with users through natural dialogue.
For example, a customer support agent can respond to an inquiry such as "Please tell me how to return the product I purchased the other day" by checking the purchase history and guiding the appropriate return procedure.
It enables dialogue that understands not only simple question answering but also the user's emotions and context.
Classification by Form: Where AI Agents Exist
Digital Agents that Run on PCs and in the Cloud
These agents operate in PC and cloud environments and process tasks in digital spaces.
For example, it performs automatic sorting of emails, information gathering from websites, and online reservation agency.
It has no physical entity and functions by manipulating APIs and databases.
Robot-Type Agents that Operate in the Real World
These agents sense the environment with sensors and act physically with actuators such as motors.
For example, a household cleaning robot recognizes the shape of the room and cleans efficiently while avoiding obstacles.
Factory assembly robots, delivery drones, and self-driving cars are also types of physical agents.
Hybrid Agents that Connect the Digital and Real Worlds
These agents have both software and hardware characteristics and operate in both digital and physical worlds.
For example, a smart home system controls physical devices such as home appliances and lighting while performing data processing in the cloud.
In response to the instruction "Wake me up at 6:00 tomorrow morning and make coffee," it can link alarm setting and coffee maker activation.
Classification by Learning Ability: How AI Agents Grow
Basic Agents that Operate According to Defined Rules
These are basic agents that operate according to clearly programmed rules.
For example, it acts on simple conditional branches such as "If the temperature exceeds 28 degrees Celsius, turn on the air conditioner."
It is characterized by predictable and stable operation, but cannot handle unexpected situations.
Agents that Learn from Experience and Become Smarter
These agents learn from data and improve their behavior patterns.
For example, a music recommendation agent learns preferences from the patterns of songs that users "like" or "skip," and gradually becomes able to make more accurate recommendations.
It is characterized by flexibility that can adapt to new situations.
Agents that Think and Evolve on Their Own
These agents evaluate the results of their actions and continuously optimize their strategies.
For example, a trading agent learns from trading results in the market and becomes able to make judgments such as "When this economic indicator is announced, we should trade more cautiously than with the previous strategy."
Through trial and error, it can acquire advanced strategies that humans have not explicitly taught.
5. Main Features and Characteristics of AI Agents
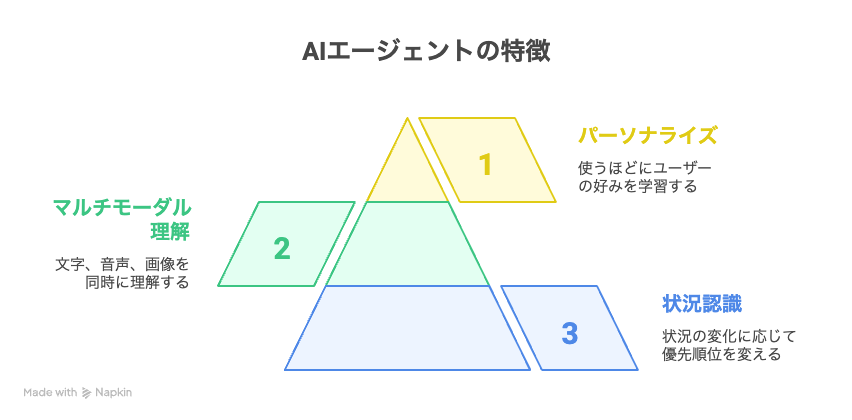
Ability to Think and Act Independently
Planning Towards Goals
AI agents understand given goals, identify necessary steps to achieve them, and create optimal action plans automatically.
For example, when asked to "Plan a weekend trip to Tokyo," the agent can assemble multiple steps such as comparing transportation options, listing recommended spots, checking weather forecasts, and finding hotels within budget—all without further input.
Adapting Priorities Based on Context
These agents adjust decisions in real-time according to changing circumstances, optimally allocating limited resources.
For instance, if an urgent meeting is scheduled, a schedule management agent can assess its importance, automatically readjust other tasks, and respond with something like "I've prioritized this high-importance meeting and rescheduled your afternoon tasks by 30 minutes."
Ability to Process Multiple Information Formats Simultaneously
Integrated Understanding Across Formats
AI agents can simultaneously process and understand information in various formats—text, images, audio, and more.
For example, a cooking assistant can analyze a photo of your refrigerator contents sent with the text "What can I make with these ingredients?", recognize the available items, and suggest appropriate recipes.
This creates seamless experiences that blend multiple senses, like navigation combining voice guidance with visual maps.
Contextual Information Delivery
These agents deliver information in the most effective format for your current situation.
They intelligently adapt their communication method—providing concise voice instructions while you're driving, detailed text and visual data when you're at your desk, or urgent notifications with haptic feedback on your smartwatch.
Ability to Provide Personalized Experiences
Learning from Interaction Patterns
AI agents learn your preferences, habits, and needs through ongoing interactions, gradually improving their predictions and recommendations.
For instance, when you request "Play something relaxing," a music agent can select genres or artists you've previously enjoyed during relaxation moments.
The experience evolves from generic suggestions to highly personalized recommendations as you continue to use the system.
Creating User-Specific Adaptations
These agents build personalized layers on top of their base AI models, tailored specifically to individual users.
A writing assistant, for example, learns your preferred level of formality, frequently used expressions, and editing patterns. When asked to "Draft an email in my usual style," it can generate text that authentically reflects your unique voice.
This enables a depth of personalization impossible with general-purpose AI systems.
6. Practical Examples of AI Agents: From Business to Daily Life
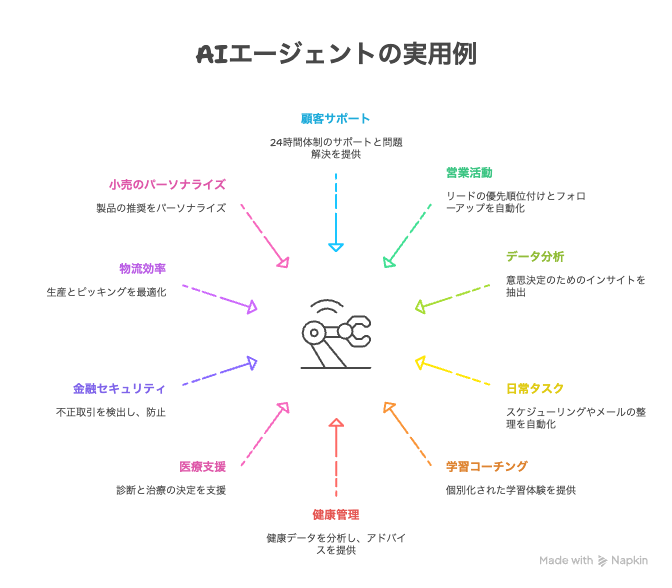
Use Cases in Companies: Improving Operational Efficiency and Customer Experience
24/7 Automated Customer Support
AI agents handle primary responses via chat or phone 24 hours a day, automating answers to frequently asked questions and simple problem-solving.
For example, in response to an inquiry such as "The product I ordered has not arrived yet," it can check the delivery status from the order number and immediately answer, "Your product is scheduled to arrive tomorrow."
Human operators can focus on complex cases, improving overall resolution rates and customer satisfaction.
Efficient Sales Activities and Strengthening Customer Relationships
AI agents analyze customer data, automatically identify and prioritize high-probability prospects (leads).
Furthermore, it automatically sends follow-up emails at appropriate times, such as "You viewed the materials last week, do you have any questions?"
It can significantly improve the conversion rate while saving sales representatives' time.
Management Decision Support Through Data Analysis
Collects and integrates information from multiple data sources and automatically extracts insights necessary for management decisions.
For example, in response to the question "What caused last month's sales to fall below expectations?", the AI agent comprehensively analyzes sales data, customer feedback, competitor information, market trends, etc., and provides specific answers such as "The main factors are the shortage of new product A and the price reduction campaign by competitors."
It visualizes complex data in easy-to-understand graphs and dashboards, supporting rapid decision-making.
Actual Success Stories
In actual business settings, major EC sites such as Amazon analyze product browsing history and purchasing patterns to realize highly accurate recommendations such as "People who viewed this product also purchased these products."
In addition, megabanks use AI agents to comprehensively evaluate the credit information and income status of loan applicants and support the judgment of examiners, thereby shortening the examination time and improving the approval accuracy.
Use Cases in Daily Life: Supporting a Convenient and Comfortable Life
Your Personal Secretary: Automating Daily Tasks
This is an AI agent that automates various tasks in daily life.
For example, if you instruct it to "Make a dentist appointment next Wednesday," it will check your calendar for available times and make a reservation with the dental clinic by phone or online.
It can also understand the content of received emails and sort them by importance, and respond to complex questions such as "If I leave at 9:00 tomorrow morning, what time should I wake up considering the traffic?"
As an evolution of Google Assistant and Apple Siri, it can autonomously handle more complex tasks.
Personalized Learning Coach
This is an AI agent that analyzes individual learning styles and progress and provides an optimal learning experience.
For example, in an English learning app, it identifies pronunciation and grammar items that you are not good at and provides individualized feedback such as "Your pronunciation of this word has improved. Next, let's focus on practicing this grammar pattern."
In response to a request to "Learn quantum mechanics from the basics," it proposes materials of appropriate difficulty in a structured manner, considering your background knowledge level, and maximizes learning efficiency by adjusting the level of detail of the explanation according to your understanding.
Health Management and Lifestyle Improvement Advisor
This is an AI agent that comprehensively manages and analyzes health data in conjunction with wearable devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers.
For example, if you say, "I've been feeling tired lately," it analyzes the past few weeks of sleep patterns, heart rate variability, activity levels, diet records, etc., and provides specific advice such as "Your sleep quality is declining. You can expect improvement by refraining from using your smartphone one hour before going to bed and lowering the temperature of your bedroom by 2 degrees."
By visualizing long-term health trends and showing how small changes in lifestyle affect health indicators, it supports sustainable health management.
Innovative Applications in Specialized Fields
Diagnostic Support and Patient Care in Medical Settings
Integrally analyzes patient test results, medical images, genetic information, past medical records, etc., to support doctors' diagnosis and treatment policy decisions.
For example, it contributes to improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment results by detecting abnormalities from MRI images and comparing them with the treatment results of similar cases to propose optimal treatment methods.
Improving the Safety and Convenience of Financial Services
Instantly detects anomalies in transaction patterns to prevent fraudulent transactions and automatically evaluates the validity of insurance claims to speed up the screening process.
For example, systems that detect "high-value payments in unusual locations" by comparing them with credit card usage history and prevent fraud damage have been put into practical use.
Improving the Efficiency of Factories and Logistics
Optimizes factory production lines based on demand forecasts and realizes efficient product picking by linking robots in warehouses.
For example, in e-commerce distribution centers, AI that has learned order patterns places related products on nearby shelves based on the information that "this product and this product are often ordered together," thereby significantly shortening picking time.
Personalization and Inventory Optimization in the Retail Industry
Analyzes sales data and inventory status in real-time and automatically determines appropriate ordering timing and quantities.
In addition, by analyzing customer purchase history and browsing behavior in detail, it recommends "products that are perfect for you" with high accuracy, simultaneously improving the customer experience and increasing sales.
For example, fashion EC sites learn customer preferences for styles, colors, and sizes, and individually notify them when new products arrive, saying "These are new items that seem to match your preferences," thereby increasing the conversion rate.
7. Benefits and Drawbacks of Implementing AI Agents
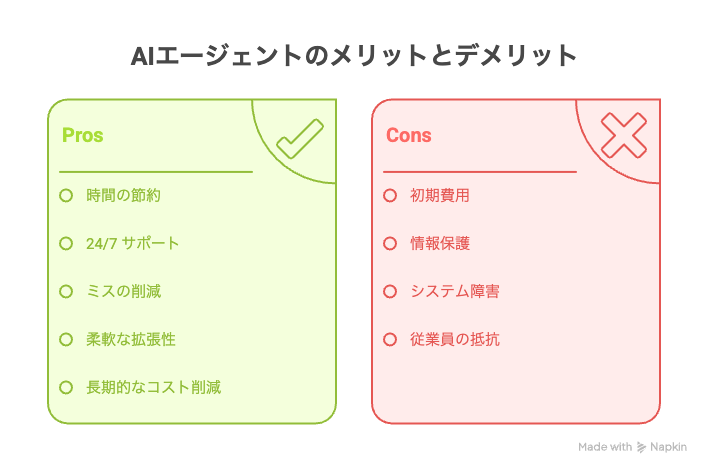
5 Benefits of Implementing AI Agents
Time Savings: Increased Efficiency Through Automation of Daily Tasks
AI agents automate routine tasks like data entry, schedule management, and information retrieval, allowing employees to focus on creative, strategic, and high-value work.
For example, a salesperson can reduce time spent on customer data entry and reporting from 10 hours to 2 hours weekly, creating more time for customer visits and proposal development.
Non-Stop Support: Available 24/7/365
Unlike humans, AI agents operate continuously without breaks, providing constant customer support and system monitoring, even during nights and holidays.
For instance, e-commerce sites can use AI to instantly respond to customer inquiries about product availability or shipping status at any hour, maintaining customer satisfaction around the clock.
Error Reduction: Preventing Human Mistakes
AI agents excel at handling monotonous, repetitive tasks that often lead to human errors such as input mistakes and oversights.
In insurance claim processing, for example, AI can automatically check application documents for deficiencies and inconsistencies, improving accuracy and reducing incorrect payment risks.
Flexible Scalability: Handling Increased Demand
When business growth leads to more users or data, you can easily scale by adjusting cloud resources to meet demand.
For example, during a major sale when e-commerce traffic increases fivefold, automatically scaling AI chatbot instances maintains response speed and ensures all customer inquiries are handled promptly.
Long-Term Cost Reduction: Sustained Investment Effect
While initial investment is required, automation reduces working hours and optimizes human resource allocation, typically enabling ROI within 1-3 years, followed by ongoing cost savings.
In call centers, AI can handle 80% of initial inquiries, reducing labor costs by 30% annually while allowing operators to focus on complex cases, creating a virtuous cycle that improves customer satisfaction.
4 Considerations and Challenges When Implementing AI Agents
Initial Costs and Expertise: Barriers to Entry
Building AI systems requires significant upfront investment for system development, data preparation, and proof-of-concept testing.
Securing specialists who understand and can operate AI technology presents another challenge, especially for smaller organizations.
Small and medium-sized enterprises often find the cost of hiring dedicated AI engineers prohibitive, forcing them to rely on external consultants.
Information Protection: Securing Sensitive Data
When AI processes customer information or confidential data, information security risks increase, requiring robust protection measures.
Essential security practices include data encryption, strict access controls, and comprehensive audit logging.
In healthcare settings, for instance, AI systems analyzing patient data require multi-layered protection, including data anonymization and encryption during all transfers.
System Failure Preparedness: Risks of Over-Reliance
Increased dependence on AI agents creates vulnerability to system failures or network outages that could halt operations entirely.
For example, if warehouse management relies completely on AI, system downtime could make manual inventory checks and shipping processes impossible, causing delivery delays.
Developing backup procedures and manual operation protocols for critical functions is therefore essential.
Internal Acceptance: Addressing Employee Concerns
Anxiety about job displacement due to AI automation can create resistance within organizations, hindering successful implementation.
When employees worry that "AI will take my job," they may withhold necessary data or cooperation.
Position AI clearly as a "partner that enhances work quality" rather than a "job replacement," and support implementation with skills training and development opportunities.
8. AI Agent Implementation Procedure: From Planning to Implementation
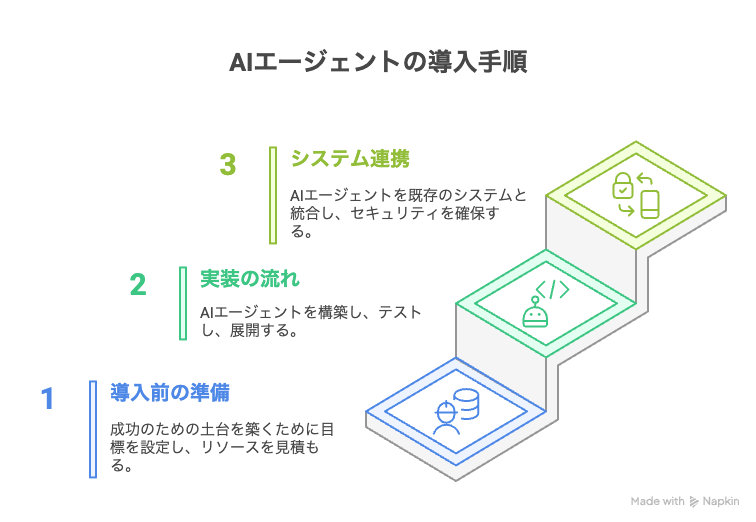
Preparation Before Implementation: Building a Foundation for Success
Setting Clear Goals and Success Metrics
Define specific objectives and establish measurable KPIs to track progress.
For example, aim for concrete targets like "Reduce customer support response time by 30%."
Selecting Optimal Tasks
Focus on tasks with the highest potential for immediate results.
Adopt a step-by-step approach that builds on small wins rather than attempting to automate everything simultaneously.
Estimating Required Budget and Personnel
Create a comprehensive investment plan covering data preparation, specialized talent acquisition, development costs, and ongoing maintenance expenses.
Implementation Flow: From Concept to Operation
Detailed Planning
Clearly document the AI agent's functions, data requirements, and performance expectations.
Use this information to design a comprehensive system blueprint.
System Construction and Adjustment
Decide between building a custom AI model or adapting an existing AI service.
For most organizations, customizing established AI platforms to fit specific needs offers greater efficiency.
Operation Verification and Performance Evaluation
Test the AI agent using realistic data to evaluate accuracy, speed, and reliability.
Pay special attention to how the system handles edge cases and unexpected inputs.
Phased Implementation and Continuous Improvement
Begin with limited pilot deployments before expanding to wider use, gathering feedback throughout.
Establish systems for ongoing AI refinement based on real-world performance data.
Integration with Existing Systems: Achieving Smooth Information Sharing
Bridging Between Systems
Connect your AI agent to internal systems and cloud services using standard APIs like REST or GraphQL.
This enables seamless information exchange across your technology ecosystem.
Centralized Data Management
Standardize data formats across different systems and implement regular synchronization processes.
Incorporate appropriate scheduling and exception handling to maintain data integrity.
Information Protection Measures
Implement robust security through authentication methods like API keys and OAuth, along with encryption and comprehensive access logging.
Apply layered security protocols, especially when handling sensitive or personal information.
9. AI Agent Products and Services Available Now
User-Friendly AI Assistants from Major Companies
Microsoft 365 Copilot - Office Task Automation Assistant
Streamlines document creation, data analysis, and meeting management across Word, Excel, and Teams.
Copilot Studio enables custom AI agent development without requiring technical expertise.
Gemini for Google Workspace - AI Support Integrated with Google Tools
Previously known as Duet AI.
Enhances Google Docs, Sheets, and Gmail with conversational document summarization, translation, and data analysis capabilities.
Amazon Q - Assistant for Simplifying AWS Cloud Service Operations
Works across AWS services, allowing natural language control of everything from code generation to business intelligence dashboard creation.
Salesforce Einstein Copilot - AI for Streamlining Customer Management Tasks
Leverages CRM data to automate sales activities and customer support through conversational interfaces.
Features enterprise-grade security and governance for handling sensitive business information.
ServiceNow Now Assist - AI for Automating Internal Support Operations
Integrates with IT support, HR, and customer service workflows to dramatically reduce response times through automated inquiry processing.
Apple Intelligence - AI for iPhone and Mac with Privacy Protection
Built-in AI for Apple devices that prioritizes privacy through on-device processing.
Developer SDK expected at the 2025 developers conference.
Meta AI - Convenient Assistant for Use Within Social Media Apps
Available in WhatsApp, Instagram, and other Meta platforms, offering image generation and information retrieval through natural conversations.
Designed with strong privacy protections.
Specialized AI Tools Focused on Specific Tasks and Fields
AI Assistants by Task - Automating Specific Jobs
Growing ecosystem of purpose-built AI agents for specific business processes, including call center automation, expense processing, and legal document review.
Industry-Specific AI - Assistants with Expertise in Specialized Fields
Domain-specific AI solutions emerging across sectors, such as Med-PaLM 2 for healthcare, BloombergGPT for finance, and Shopify Sidekick for e-commerce management.
Single-Function Specialized AI - Thoroughly Streamlining One Task
Highly focused tools delivering exceptional results in narrow domains, like Clarifai for image analysis, Otter.ai for meeting transcription, and Eightify for video content summarization.
10. The Future of AI Agents: How Will They Change and Be Utilized?
How Will AI Capabilities Evolve in the Future?
Multimodal Understanding: Beyond Text
Future AI will seamlessly process multiple information sources simultaneously—images, audio, video, and sensor data—alongside text.
For instance, AI will analyze meeting recordings to understand not just what was said, but also participants' expressions, tone of voice, and emotional context.
Autonomous Decision-Making and Action
AI agents will increasingly set goals, plan strategies, and execute tasks independently with minimal human guidance.
We'll see multiple AI agents collaborating to solve complex problems, working systematically toward long-term objectives through coordinated efforts.
Transparent Reasoning and Explainability
AI will provide clear explanations for its decisions in human-understandable terms.
Interfaces will become standard that reveal the data foundation behind conclusions and visually map cause-effect relationships, making AI reasoning transparent.
How Will Business Change?
Evolution of AI Service Models
Beyond traditional subscriptions, usage-based and results-based pricing models will become prevalent.
An interconnected ecosystem will emerge where specialized AI functions combine through robust API marketplaces, enabling more sophisticated solutions.
Workforce Transformation
As routine tasks become automated, new roles will emerge focused on AI oversight, prompt engineering, and managing human-AI collaboration.
Effective AI utilization will become a core competency across most professions, fundamentally changing skill requirements.
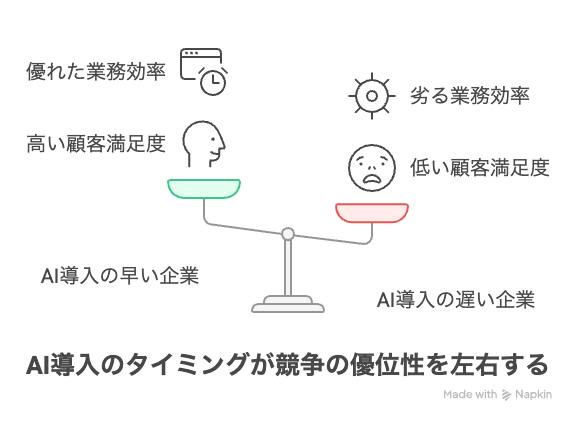
Competitive Differentiation
Companies that rapidly adopt and effectively implement AI agents will gain significant advantages over slower competitors.
Organizations with high-quality data assets and the capability to properly train AI systems will achieve superior customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Societal Impact and Ethical Considerations
Establishing Accountability Frameworks
Robust audit trails for AI decisions and actions will become essential for tracing responsibility when issues arise.
New legal and social frameworks will emerge to clearly define accountability for AI judgments across various contexts.
Privacy Protection Evolution
Data minimization principles will gain prominence, using only essential information to train and operate AI systems.
On-device processing and advanced encryption technologies will become standard practice, reducing cloud-based privacy vulnerabilities.
Balanced Human-AI Collaboration
To counter automation bias and over-reliance on AI, governance systems will ensure humans maintain final authority for critical decisions.
Regular human oversight of AI judgments will be built into workflows to maintain appropriate checks and balances.
Summary
AI agents are rapidly transforming both business and personal domains through their contextual understanding and autonomous capabilities.
The market is expanding with solutions from major platforms like Microsoft Copilot, Google Gemini, and Amazon Q, alongside specialized industry-specific offerings.
While AI agents promise significant productivity improvements and cost reductions, successful implementation depends on addressing privacy concerns, ethical considerations, and managing organizational change effectively.
Looking ahead, advances in multimodal technology and reinforcement learning will grant AI agents greater autonomy, fundamentally reshaping social and industrial structures.
For organizations adopting AI agents, success hinges on clear goal-setting, phased implementation, and comprehensive governance frameworks.